Welcome to a world where machines don’t just hum and whir on command—they analyze, learn, adapt, and even collaborate with their human coworkers. If you’ve ever imagined a factory floor brimming with robotic arms that diagnose their own issues, conveyor belts that optimize speed based on real-time demand, and intelligent systems that manage production schedules with uncanny accuracy—congratulations, you’ve already pictured smart manufacturing powered by artificial intelligence (AI).
Once the stuff of sci-fi novels and optimistic TED Talks, AI in manufacturing is no longer a futuristic fantasy. It’s here. And it’s transforming how we build, move, and scale products on a global level. From small shops that automate repetitive tasks to multibillion-dollar corporations investing in fully autonomous production lines, AI is driving what experts call the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
But what does all this really mean for businesses, workers, and the rest of us? Is AI a benevolent assistant, helping humans shed menial tasks and unlock their creative potential? Or is it a cold, calculating force gradually phasing out human involvement in pursuit of efficiency? Depending on who you ask, it’s either the best thing to happen to manufacturing since the assembly line—or the beginning of a much deeper philosophical shift about work, purpose, and intelligence itself.
In this blog post, we’ll dive deep into the state of AI in smart manufacturing, highlight some of the latest real-world innovations, and even dip our toes into a few philosophical waters. With recent news stories, research-backed insights, and a few light-hearted musings along the way, consider this your roadmap through the brave new world of intelligent industry.
Let’s plug in.
What Is Smart Manufacturing
(And Why Should You Care)?
Smart manufacturing refers to the use of advanced technologies—including AI, machine learning, robotics, and data analytics—to optimize production processes, reduce waste, and improve efficiency. It’s a paradigm shift from traditional automation to intelligent systems that can self-correct, learn from data, and adapt in real time.
In a typical smart factory, every element of the manufacturing process—from sourcing materials to final quality checks—is monitored, analyzed, and enhanced by digital systems. These factories are often powered by IoT devices that gather real-time data, cloud platforms that centralize intelligence, and AI algorithms that draw insights to optimize performance.
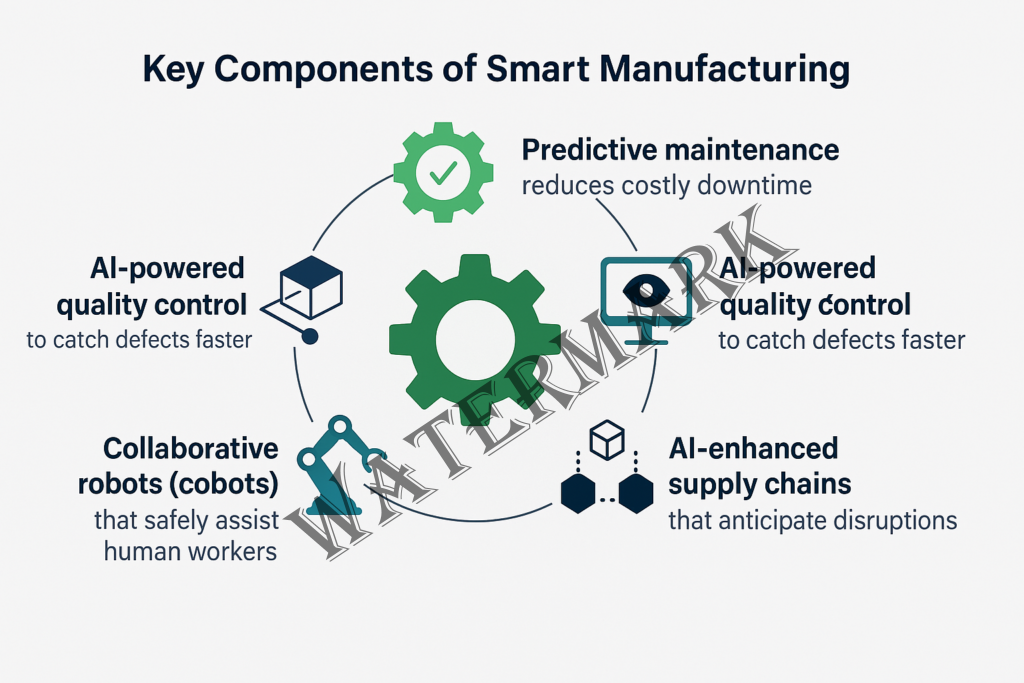
Key components include:
- Predictive maintenance that reduces costly downtime by identifying early signs of machine failure.
- AI-powered quality control to catch defects faster and with greater precision than manual inspection.
- Digital twins—virtual replicas of physical systems—to simulate and optimize production workflows.
- AI-enhanced supply chains that anticipate market trends and disruptions to improve agility.
- Collaborative robots (cobots) that safely assist human workers, taking on tasks that are repetitive, dangerous, or ergonomically challenging.
The ultimate goal? To create a manufacturing ecosystem that is not just automated—but autonomous, responsive, and continuously improving.
Real-World Examples of AI in Manufacturing
Schneider Electric: Investing in the Smart Grid
In March 2025, Schneider Electric announced a bold $700 million investment in U.S. manufacturing facilities to meet the growing energy demands of AI infrastructure (Reuters, 2025). With AI applications consuming enormous amounts of power, Schneider is prioritizing resilient, digitally enabled power distribution systems. It’s a move that speaks to a broader trend: manufacturing and energy are becoming increasingly interconnected through AI.
Beyond just hardware, Schneider is using AI internally to monitor power use in real-time and forecast equipment failures. By 2027, the company hopes to build not only smarter grids but smarter factories—where energy consumption is optimized, waste is minimized, and performance is constantly refined through AI feedback loops.
Apple’s AI-First Facility in Houston
Apple is making waves in the AI manufacturing space, too. In 2025, the tech giant announced a new 250,000-square-foot server manufacturing facility in Houston. This factory will focus specifically on building infrastructure for Apple’s AI systems, expected to power next-generation iCloud services, Siri, and potentially even autonomous systems.
Apple’s new venture isn’t just a tech play—it’s a statement. The facility is expected to create thousands of jobs and support a $500 billion investment plan over the next four years, tying AI innovation to local economic growth and workforce development (Houston Chronicle, 2025).
Hyundai’s $7.59 Billion Smart Metaplant
Hyundai Motor Group is taking automation to another level with its $7.59 billion “Metaplant” in Georgia. This futuristic facility will house AI systems that not only manage manufacturing lines but learn and evolve over time. Hyundai is betting big on AI to streamline logistics, monitor safety, and even automate quality control using high-resolution imaging powered by deep learning.
As part of its commitment to innovation, Hyundai is integrating AI not only into the machinery but also into the design of the plant itself, using simulation software to anticipate traffic patterns, energy needs, and optimal layout configurations before a single part is produced (Axios, 2025).
A Light Dose of Philosophy:
Will AI Replace Us?
Let’s take a step back. The deeper question behind all this is: What is the role of humans in a machine-optimized world? Will AI replace the factory worker—or redefine them?
There’s a growing school of thought suggesting AI won’t eliminate humans from manufacturing, but elevate them. By automating repetitive or dangerous tasks, AI frees up workers to focus on creativity, supervision, and strategic decision-making. We may be moving toward an age of “augmented manufacturing” where human insight and machine intelligence dance together in harmony.
But this philosophical debate goes deeper. As machines become more autonomous, we must ask: What happens to meaning in work when work changes? For centuries, labor has been tied to identity. If AI gradually absorbs more responsibility, will we need to reimagine fulfillment—not just employment?
It’s not about resisting change, but navigating it wisely. The key lies in designing systems where technology serves humanity, not the other way around.
Ethical Considerations in AI Manufacturing
As AI grows more powerful and pervasive, ethics must keep pace. In manufacturing, this means developing AI systems that are transparent, inclusive, and aligned with human values.
A few pressing ethical concerns:
- Bias in Decision-Making: AI models trained on flawed data can unintentionally favor certain outcomes. If a system determines hiring, shift scheduling, or performance evaluations, its algorithms must be fair and auditable.
- Job Displacement and Economic Equity: While AI may create new roles, it can also displace workers who lack digital skills. Supporting reskilling programs is a moral imperative—not just a business strategy.
- Environmental Responsibility: AI can reduce energy waste, but it can also increase computational demand. Striking a balance between innovation and sustainability will define the next phase of ethical smart manufacturing.
Transparency is another critical pillar. Workers and stakeholders should understand how AI systems make decisions. The rise of “explainable AI” (XAI) is helping bridge the gap between black-box algorithms and human trust.
In essence, ethical AI in manufacturing isn’t about making machines less intelligent—it’s about making their intelligence more accountable.
Common Challenges in AI Manufacturing Adoption
Let’s not paint an overly rosy picture—implementing AI in manufacturing comes with its own set of challenges:
- Data Quality & Integration: AI thrives on data. But outdated or siloed systems make it hard to feed accurate information into AI models.
- Cybersecurity Risks: As smart factories become more connected, they also become more vulnerable. Protecting networks from cyberattacks is a top priority.
- Skill Gaps: AI doesn’t replace human workers—it changes what they need to know. Upskilling the workforce is essential for successful implementation.
- Cultural Resistance: Not everyone welcomes robots with open arms. Change management is a human challenge, not a technical one.
Despite these challenges, the momentum is undeniable. A 2024 study in Applied Sciences found that smart factories leveraging AI reported up to 45% higher efficiency and 30% fewer errors within two years (Hussain et al., 2024).
What the Research Says
AI’s role in manufacturing is backed by a growing body of scientific research:
- A 2024 article in ScienceDirect emphasized how deep learning models are revolutionizing predictive maintenance, helping reduce downtime by up to 60% in complex production systems.
- A Nature Machine Intelligence paper urged the adoption of explainable AI to ensure human oversight, especially in safety-critical environments like aerospace and pharmaceuticals.
- MDPI Applied Sciences explored how computer vision powered by neural networks is setting new benchmarks in real-time defect detection.
This research doesn’t just validate AI’s potential—it offers a roadmap for implementation grounded in evidence.
The Road Ahead: Trends to Watch
Looking forward, several trends are shaping the next phase of AI in manufacturing:
- Federated Learning: Allowing AI to be trained on decentralized data while preserving privacy—ideal for multi-site global manufacturers.
- Edge AI: Processing data at the machine level for instant feedback and reduced latency.
- Green AI: Optimizing systems not just for profit, but also for planet. Expect more AI systems tuned for carbon reduction and circular production.
- Human-Centered AI: Designing systems that augment rather than replace human roles, with user-friendly interfaces and accessible analytics.
AI isn’t just learning to build things—it’s learning to build better.
Final Thoughts:
A Human Future with Smart Machines
AI in manufacturing is not just about cutting costs or speeding up output. It’s about rethinking the nature of production itself. The factory is evolving from a place of repetition to a space of intelligence. From the rhythmic clang of metal to the subtle hum of sensors and algorithms, the modern factory tells a new story—one of synergy between human minds and digital ones.
As we continue integrating AI into every bolt and blueprint, one truth remains: technology should serve people—not replace them. So, will AI take over factories? In many ways, it already is. But should we fear it? Not if we guide it with ethics, empathy, and imagination.
Let’s build smarter—together.
References
- Axios. (2025, March 20). How Hyundai Motor Group is driving U.S. jobs, innovation and more. Retrieved from https://www.axios.com/sponsored/how-hyundai-motor-group-is-driving-us-jobs-innovation-and-more
- Fernandez, R., Singh, S., & Kumar, D. (2024). Towards explainable AI in manufacturing systems. Nature Machine Intelligence, 6(1), 22–31. https://www.nature.com/articles/s44334-024-00006-9
- Houston Chronicle. (2025, March 15). Apple’s new manufacturing facility will bring thousands of jobs to Houston, fuel AI boom. Retrieved from https://www.houstonchronicle.com/business/article/apple-houston-ai-server-manufacturing-20183749.php
- Hussain, M., Patel, R., Zhao, Y., & Lin, J. (2024). Impact of AI-driven manufacturing on efficiency: A meta-analysis. Applied Sciences, 13(3), 1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031002
- Nguyen, D., & Park, J. (2024). Deep learning challenges in smart manufacturing. Applied Sciences, 14(2), 8239. https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/14/2/8239
- Reuters. (2025, March 25). Schneider Electric to invest over $700 million in US to power AI boom. Retrieved from https://www.reuters.com/business/schneider-electric-invest-over-700-million-us-power-ai-boom-2025-03-25/
- Zhou, Y., Wang, K., & Li, Q. (2024). Artificial intelligence in manufacturing: State of the art and perspectives. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 82, 305–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmsy.2024.03.015
Additional Readings
- Advanced Technology Services. (2025). 13 smart manufacturing trends for 2025 and beyond. Retrieved from https://www.advancedtech.com/blog/smart-manufacturing-trends/
- Forbes Technology Council. (2023, December 6). How companies can succeed with AI in smart manufacturing. Forbes. Retrieved from https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestechcouncil/2023/12/06/how-companies-can-succeed-with-ai-in-smart-manufacturing/
- Rockwell Automation. (2025). 5 key trends redefining smart manufacturing in 2025. Retrieved from https://www.rockwellautomation.com/en/company/news/blogs/smart-manufacturing-trends-2025.html
Additional Resources
- AI Business. (2025). Industrial manufacturing news and analysis. Retrieved from https://aibusiness.com/verticals/industrial-manufacturing
- Association for Advancing Automation. (2025). AI industry insights and tools. Retrieved from https://www.automate.org/ai/news
- SEMI. (2025). Smart manufacturing updates and reports. Retrieved from https://www.semi.org/en/industry-groups/smart-manufacturing/news